Menu
Close

Menu
Close
Early Pregnancy Scan
A comprehensive early assessment delivered within a consultant-led care pathway
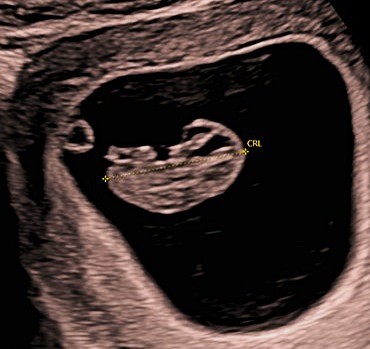
The Early Pregnancy or Viability Scan is performed in the first trimester, most commonly between 7 and 10 weeks of pregnancy. The scan is carried out to confirm that the pregnancy is developing within the womb (intrauterine), to assess viability by demonstrating a normal fetal heart rhythm where appropriate, and to ensure that the supporting structures of the pregnancy appear healthy. It also confirms the number of babies and assesses early development in relation to gestational age.
At The Pregnancy Clinic, early pregnancy scans are delivered within a consultant-led care pathway, with time for explanation, discussion, and reassurance. Where findings are early or uncertain, clear guidance and appropriate follow-up planning are provided to ensure that conclusions are not rushed and that you feel supported throughout.
Book your consultant-led anomaly scan today for expert assessment, reassurance and high-quality pregnancy care.

FAQs
What is the purpose of an early pregnancy scan?
The early pregnancy scan is performed to confirm that the pregnancy is located within the uterus and to assess early development. It allows confirmation of viability where appropriate, identification of the number of babies, and assessment of early pregnancy structures. This scan provides reassurance in early pregnancy and helps guide ongoing care.
Who should consider having an early pregnancy scan?
An early pregnancy scan may be considered by anyone seeking reassurance following a positive pregnancy test. It is particularly helpful for women who have experienced bleeding or pain, have had a previous miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy, have conceived following fertility treatment, or are uncertain about their pregnancy dates.
When is the best time to book an early pregnancy scan, and what can be seen at different stages of early pregnancy?
The most appropriate time to book an early pregnancy scan depends on how far along the pregnancy is and what information you are hoping to obtain.
- At 5–6 weeks of pregnancy, the scan may show a small gestational sac within the uterus and, in many cases, a yolk sac. At this stage, it is often too early to reliably see a fetal heartbeat, and this can be entirely normal.
- From around 6½–7 weeks onwards, a fetal pole is usually visible and a heartbeat can typically be detected.
- Between 7 and 10 weeks, the scan provides more definitive reassurance. A heartbeat should be clearly seen, early development can be assessed, and the number of babies can be confirmed.
For most women seeking reassurance and a clear outcome from a single visit, booking the scan from 7 weeks of pregnancy onwards is ideal. If the scan is performed earlier, a follow-up scan may sometimes be recommended.
How is the early pregnancy scan performed?
The scan is usually performed initially through the abdomen. In very early pregnancy, or if views are limited, an internal (transvaginal) scan may be recommended to obtain clearer images. This is a safe and commonly used technique and will only be performed with your understanding and consent.
Do I need a full bladder for the scan?
A moderately full bladder can help improve visualisation during the abdominal part of the scan. You do not need to be uncomfortably full, and you may be asked to empty your bladder during the appointment if required.
What happens if a heartbeat is not seen at the early pregnancy scan?
If a heartbeat is not seen, the findings are interpreted carefully in the context of how far along the pregnancy is and the scan appearances.
- Very early in pregnancy (before 7 weeks), it is common not to see a heartbeat, and this does not necessarily indicate a problem.
- If the pregnancy appears earlier than expected, or the findings are inconclusive, a repeat scan is usually recommended after 7–14 days to allow time for further development.
- If the scan findings meet established medical criteria for a non-viable pregnancy, this will be discussed with you sensitively and clearly.
Throughout this process, you will be fully supported, with clear explanations of the findings, what they mean, and the next steps. Where appropriate, we will also advise on follow-up care and liaise with NHS early pregnancy services to ensure continuity and safety.
What if my dates are uncertain or my menstrual cycles are irregular?
If your dates are uncertain or your cycles are irregular, this is taken into account when interpreting the scan findings. In early pregnancy, development does not always match the date of the last menstrual period, and this can be entirely normal.
If the pregnancy appears earlier than expected, this does not necessarily indicate a problem. Where appropriate, a follow-up scan may be recommended after a suitable interval to allow clearer assessment and provide reassurance.
Can the early pregnancy scan assess the risk of genetic or chromosomal conditions?
Assessment of the risk of chromosomal conditions is not performed at the early pregnancy scan. This is undertaken later in pregnancy at the 11–13 week nuchal scan. Where appropriate, non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) can be offered from 10 weeks of pregnancy onwards.
Can NIPT be performed at the same visit as an early pregnancy scan?
Yes. If you are at least 10 weeks pregnant, NIPT can be performed at the same appointment. Testing earlier than this may increase the likelihood of an inconclusive result. Testing for fetal sex may be possible earlier.